Straight Arm Plank
How to do Straight Arm Plank?
The straight arm plank is a foundational core exercise that strengthens the abdominal muscles, shoulders, and stabilizers throughout the body. By maintaining a high plank position with your arms straight, this exercise engages the entire body, promoting strength, stability, and endurance. It’s a great exercise for improving posture, core strength, and functional fitness.
Steps to Perform a Proper Straight Arm Plank
1. Starting Position:
• Begin by getting into a push-up position with your hands placed directly under your shoulders, fingers spread wide for stability.
• Extend your legs straight behind you with your feet hip-width apart. Keep your body in a straight line from your head to your heels, engaging your core, glutes, and quads to maintain this alignment.
2. Body Alignment:
• Your body should form a straight line, avoiding any sagging of the hips or arching of the lower back. Ensure your shoulders are stacked directly over your wrists.
• Keep your head in a neutral position, looking down at the floor to prevent neck strain.
3. Engage Your Core:
• Tighten your abdominal muscles by pulling your belly button toward your spine. This core engagement is crucial to maintaining proper form and preventing lower back strain.
4. Hold the Position:
• Hold this straight arm plank position for the desired amount of time, focusing on maintaining body alignment and breathing steadily throughout.
5. Complete the Set:
• Once you’ve held the plank for your goal duration, gently lower your knees to the floor to rest, or move into a different exercise.
Benefits of Straight Arm Planks
• Strengthens the Core: The straight arm plank is one of the best exercises for building core strength and stability, engaging the abdominals, obliques, and lower back muscles.
• Improves Posture: By engaging the core, shoulders, and glutes, this exercise helps promote better posture by reinforcing proper alignment.
• Builds Shoulder Stability: The straight arm plank requires shoulder engagement to support the body, improving shoulder stability and strength.
• Full-body Engagement: Although primarily a core exercise, the straight arm plank engages multiple muscle groups, including the legs, glutes, chest, and arms.
• Increases Endurance: Holding a plank for extended periods challenges muscle endurance, especially in the core and upper body.
• Reduces Risk of Injury: A strong core is essential for preventing lower back injuries and improving overall functional strength in daily activities.
• No Equipment Needed: The straight arm plank can be done anywhere, making it a versatile exercise for home workouts, outdoor training, or the gym.
Tips for the proper execution of Straight Arm Plank
Core Engagement: Keep your core tight throughout the exercise to avoid letting your lower back sag. Imagine bracing your abdominals as if someone is about to punch your stomach.
Neutral Spine: Maintain a straight line from head to heels. Avoid looking forward or letting your head drop—your neck should stay in line with your spine.
Shoulder Positioning: Your shoulders should stay directly above your wrists, not leaning forward or backward. This will help engage your shoulders and prevent wrist strain.
Controlled Breathing: Breathe steadily throughout the plank. Inhale deeply through your nose and exhale through your mouth, using your breath to help stabilize your core.
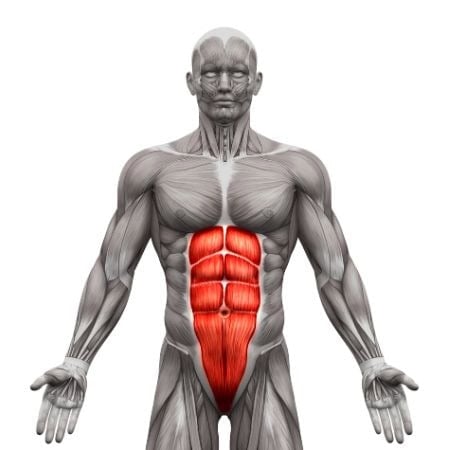
Muscles worked when doing Straight Arm Plank
Primary Muscles:
•Core: Abdominals and obliques (for stabilization)
•Shoulders: Anterior deltoids
•Chest: Pectoralis major (engaged to support the upper body)
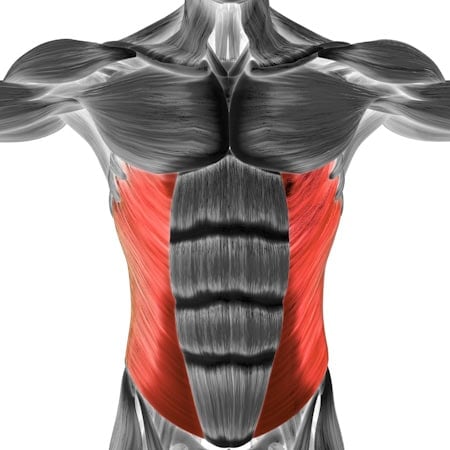
Secondary Muscles:
•Glutes: Engaged to maintain body alignment and support the lower back
•Quadriceps: Engaged to keep the legs straight and stabilize the lower body
•Lower Back: Erector spinae (supports the spine and helps prevent sagging)
•Triceps: Help support the arms and maintain a straight arm position
•Wrists and Forearms: Stabilize the upper body during the plank
Primary Muscle(s):
Secondary Muscle(s):
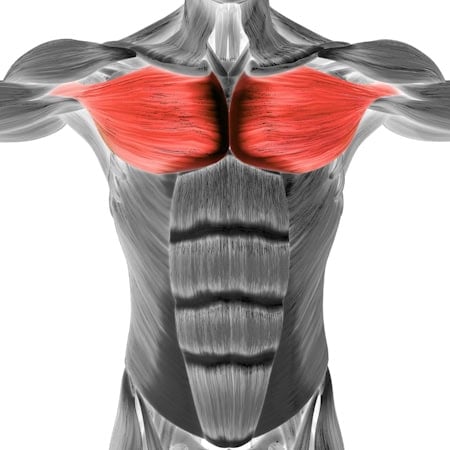
Middle chest
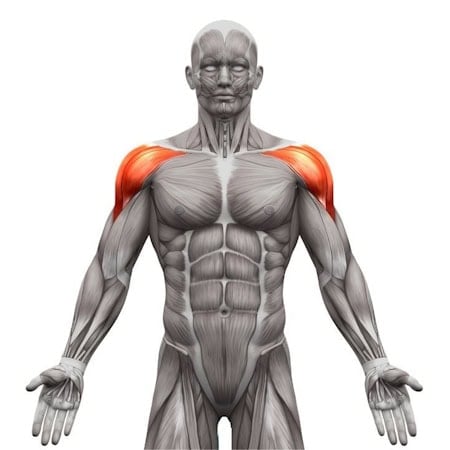

Anterior delt
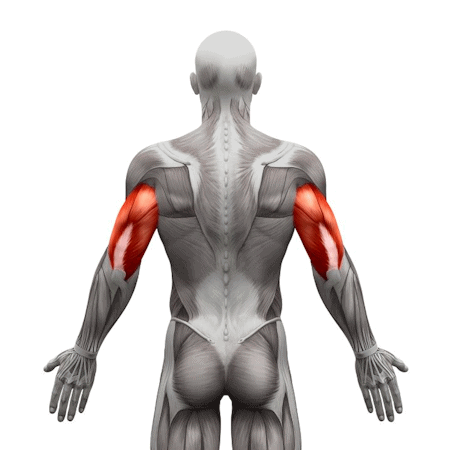
Triceps
Equipment needed for Straight Arm Plank
No equipment needed for this exercise.
Adjust the difficulty of Straight Arm Plank
How to make Straight Arm Plank harder?
How to make Straight Arm Plank easier?
How to make Straight Arm Plank harder?
To make Straight Arm Plank harder:
-
Increase Duration: Hold the plank for a longer period, such as 60 seconds or more, to challenge your endurance and core strength.
-
Add Shoulder Taps: While in the plank, alternate lifting one hand to tap your opposite shoulder, engaging your core and adding an element of instability.
-
Raise One Arm or Leg: Lift one arm or one leg while maintaining the plank position to increase the challenge on your core and balance.
-
Weighted Plank: Wear a weighted vest or place a small weight plate on your back to add resistance, making the exercise more difficult.
How to make Straight Arm Plank easier?
To make Straight Arm Plank easier:
-
Perform on Your Knees: Lower your knees to the floor while keeping your arms straight. This reduces the load on your core and upper body, making it easier to maintain proper form.
-
Shorten the Duration: If you’re new to planks, start with shorter holds (10-15 seconds) and gradually increase the time as your strength improves.
-
Use an Elevated Surface: Place your hands on an elevated surface like a bench or step to reduce the intensity while still practicing the plank form.